Environmental Simulations
Throughout their daily use, assemblies, devices, and systems are subjected to an extremely wide range of natural and artificial environmental conditions. Accordingly, these products, as well as the used materials, need to meet strict durability requirements. In order to address this, I²PS can conduct tests designed to evaluate the environmental resistance of products by using testing systems to simulate the corresponding conditions during shipping, storage, and operation, thus providing the basis for evaluating the serviceability of these products even under extreme environmental conditions.
|
The climatic environmental conditions under which technical devices are operated and which these devices must be able to withstand can vary enormously depending on the relevant application and location of use. Examples include climatic conditions that vary geographically (e.g., humidity, temperature, etc.), industrial environments with specific corrosive loads (e.g., atmospheres containing sulfur), and "harsh" production environments (resulting from high temperatures, exposure to fluids, and mechanical loads).
In order to test whether your devices are able to withstand these adverse conditions, we can age them under an extremely wide range of climatic conditions in our testing systems. This makes it possible to examine the resistance of a product against damaging climatic conditions with the use of controlled and reproducible test conditions. More specifically, our test chambers can produce temperatures of -70 °C to 240 °C and a relative humidity of 4% to 100%. In addition, we have high-temperature ovens (muffle furnaces) that can be operated at temperatures higher than 1,000 °C for special tests at high temperatures (e.g., ashing, residue on ignition, determination of filler content, heat treatments, etc.).
Meanwhile, the effect of atmospheres containing sulfur can be tested with a Kesternich test, in which acid rain conditions are simulated with an alternating sulfur dioxide atmosphere to which DUTs are exposed. The effect of "pure" condensate can also be tested, as well as icing on DUTs with an icing test. Furthermore, open-air weathering tests can also be performed following consultation.
.
|
Relevant Standards:
DUTs and Specimens: |
|
One of the best known corrosion tests is the salt spray test. This test is normally used as an accelerated corrosion test on metals and metal alloys. The reason the salt spray test has such a strong corrosive attack is the fact that it uses a highly concentrated electrolyte than has an enormous influence on the rate of corrosion. Within this context, the test's intensity depends on the salt concentration, the test temperature, and the test cycle configuration used. In addition, there are also many other test methods that can be used to evaluate the corrosion behavior of DUTs.
Our Services:
- Condensed water test climates and condensed water alternating climates
- Condensed water test climates with a sulfur dioxide atmosphere (Kesternich test)
- Salt spray tests, constant or cyclic, at test chamber temperatures from +25 °C to +50 °C, 2 test chambers with a volume of approx. 2 cubic meters each
|
Relevant Standards:
DUTs and Specimens: |
|
Impact tests are used to test and classify (e.g., IK code) the protection of a metal or plastic enclosure against dynamic mechanical loads. Within this context, the corresponding impact energy is transmitted in a variety of manners depending on the standard being used, with a drop hammer, spring-operated impact hammer, and pendulum impact tester being some examples. In fact, the type of impact element that needs to be used is defined in detail in the relevant standard (material, shape, dimensions, weight, etc.). In addition to impact tests, drop tests (e.g., ball drop tests) from a defined height onto products with and without outer packaging can be performed the way they are described in a variety of testing and product standards.
Finally, we perform impact tests not only on components and devices, but also on specimens in order to determine the characteristic values of the corresponding material. Within this context, we particularly use Charpy and Izod impact tests, which measure energy absorption during an impact test with a pendulum impact tester on notched or unnotched specimens.
|
Relevant Standards: |
|
The purpose of mechanical shock tests is to simulate conditions that can occur during the transport or operation of parts, devices, and/or equipment. Within the context of these tests, the important aspect is how the structure reacts to excitation displacements and accelerations. In fact, the ability of the structure to transmit and dampen mechanical shock, as well as its resistance to it, can be determined.
In addition, we offer online monitoring services that provide additional information on the DUT during testing.
We conduct both shock and bump tests in conformity with international standards and customer-specific standards and specifications.
- Climate / temperature chamber with 1,200 liter chamber volume
- 10 % rH bis 95 % rH
- -70 °C until +180 °C
- 5 °C / minute Temperature gradient heating as cooling
- Various clamping devices: Headexpander, test cube, test angle, etc.
- Max. test specimen weight up to 900 kg (depending on test profile)
- Vibration testing device with sliding table in different power ranges with max. forces up to 55 kN
- Frequency range from 5 Hz to 2500 Hz up to a max. acceleration of 250 g (mass-dependent)
- Combined load testing of vibration, temperature and humidity
- Laser vibrometer and accelerometer for monitoring the dynamic parameters defined in the test conditions
- Various excitation modes such as sine, noise, shock, sine on noise etc.
- Functional monitoring of the DUT under dynamic stress such as contact monitoring or similar
- Temperature measurement, current loading of contacts
- Resonance search and dwell test
|
Relevant Standards: DIN EN 60068-2-27, ISO 16750-3, DIN EN 61373 (VDE 0115-106), MIL-STD-810, RTCA/DO-160D Section 7 DUTs: |
|
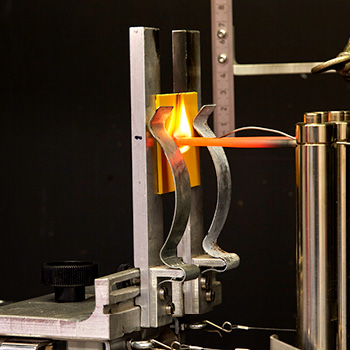
The behavior exhibited by materials when subjected to abnormal heat or fire is crucial when it comes to the operational reliability and safety of a product, especially in the case of electrical products. Accordingly, a large number of methods that can be used to test the flammability properties of materials can be found in IEC, DIN EN, ASTM, and UL standards. We can perform glow wire tests (GWT), GWFI, GWIT, GWEPT, needle flame tests (NFT), and horizontal and vertical flame tests in conformity with IEC/UL classifications HB, V0, V1, V2, 5VA, and 5VB. Depending on the specific testing method used, these tests are performed on material specimens, components, or complete devices.
|
Relevant Standards: DIN EN / IEC 60695-2-10, -11, -12, -13, 60695-11-5, 60695-11-10, 60695-11-20, 60335-1
DUTs: |